
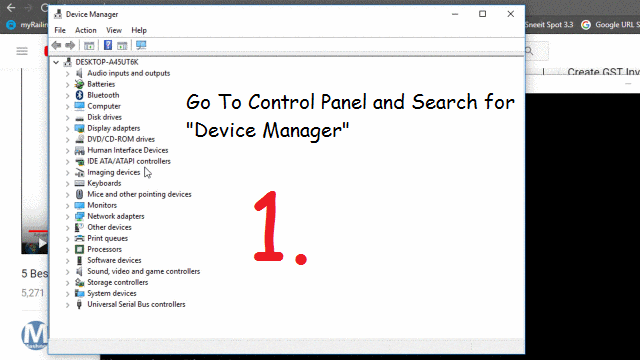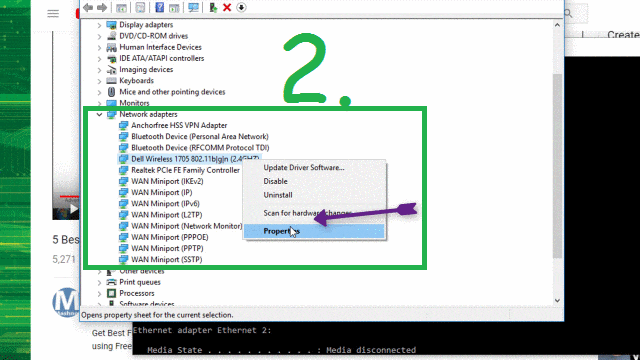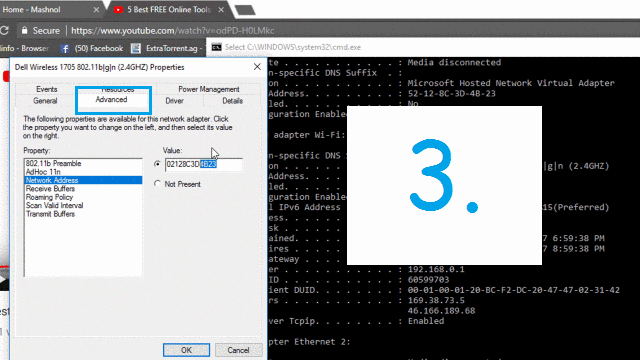
#MACSPOOF SOFWARE GENERATOR#
An integrated generator creates randomly generated suggestions on request. The original identifier is stored in the tool as well as the altered MAC address. The Freeware tool offers an overview of all connections, displays the current MAC addresses of the hardware in use, and includes a function that allows you to change it with the push of a button.
#MACSPOOF SOFWARE MAC OS X#
Linux, Mac OS X and Microsoft Windows all allows users to establish LAN connections without requiring a MAC address.
#MACSPOOF SOFWARE MANUAL#
Masking the hardware addresses of individual computers behind authorized network users requires nothing more than a manual configuration of the network settings on the respective operating system. In reality, MAC whitelists offer very little protection. But MAC spoofing enables hackers to get around security measures like this. WLAN networks can also restrict access to known network devices using MAC filters.

If it’s an unknown address, the switch blocks the respective port and stops the communication attempt.

Once a connection has been established from one segment to another, the intermediate coupling element checks the MAC address of the sender device and matches it with an administrator-created whitelist. Switches can separate big networks into smaller segments. At the network level, linking elements such as Ethernet switches via port security provide the opportunity to filter network data traffic on the OSI layer 2. To protect IT systems from internal and external dangers, administrators sometimes implement security measures that restrict access to the LAN to authorized devices. Basically, spoofing is a resolution strategy for troubleshooting – but in most cases, it’s used for the infiltration of foreign systems and illegal network activities instead. Other than MAC addresses, other popular targets for spoofing attacks are the internet protocol (IP), domain name system (DNS), and address resolution via Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). Hackers use this method of attack to conceal their own identity and imitate another.

Every MAC address includes 48 bits, or 6 bytes, and is arranged in the following pattern: 00:81:41:fe:ad:7e.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
